Absolute Reticulocyte Count
"Absolute Reticulocyte Count & Index - For Anemia" is a mobile app designed to help medical practitioner to calculate absolute reticulocyte count and reticulocyte index. This "Absolute Reticulocyte Count & Index - For Anemia" will help medical practitioner to evaluate the body response toward anemia. Increased reticulocyte count reflects ongoing or recent red blood cell (RBC) production activity. A decreased reticulocyte count reflects decreased RBC production. The reticulocyte index is another parameter that provides an assessment for adequate bone marrow response to anemia.
There are several features of "Absolute Reticulocyte Count & Index - For Anemia", namely:
- Simple and very easy to use hematology app.
- Precise calculation of absolute reticulocyte count and reticulocyte index.
- It is totally free. Download now!
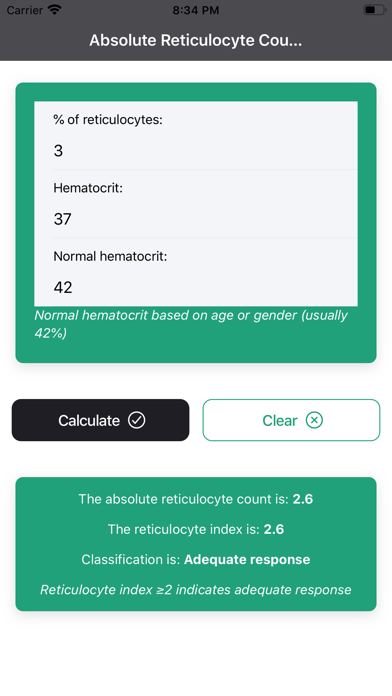
The reticulocyte count is used to estimate the degree of effective erythropoiesis, which can be reported as absolute reticulocyte count or as a reticulocyte percentage. In general, reticulocytes mature within one day of being released from bone marrow; however, in the setting of stress erythropoiesis, as in a high erythropoietin level (eg, in persons with severe anemia), reticulocytes are prematurely released from bone marrow to the blood circulation, increasing the number of days that reticulocytes stay in the blood circulation (maturation time of reticulocytes in days) and resulting in a spuriously high reticulocyte count. The reticulocyte index, or reticulocyte production index, is a calculation that helps to alleviate the effect of the premature release of reticulocytes by taking into account maturation time of reticulocytes (ie, correction factor), in addition to correcting for the degree of anemia. You can calculate both reticulocyte count & index easily with this "Absolute Reticulocyte Count & Index - For Anemia" app.
Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4190718/#__ffn_sectitle
Disclaimer: All calculations must be re-checked and should not be used alone to guide patient care, nor should they substitute for clinical judgment